Various circumstances need the connecting of various metal pieces. How To Bond Metal To Metal Without Welding? many people question.
Metal joining without welding is challenging, but in this quick instructional, we’ll go over the basics.
Welding is a common method for accomplishing this, but there are other choices as well. Continue reading to understand how to mend a fractured metal without the use of welding.
Processes like as soldering, brazing, and riveting, as well as the use of adhesives and even nanomaterials, are all examples.
How To Bond Metal To Metal Without Welding
Welding isn’t always the best approach to unite two metals. Learning to forge metal without a welder is not as dangerous or risky.
Welding is potentially hazardous due to the risk of electric shock, burns from high temperatures, and poisonous gas problems.
It is also a pricey technique due to the cost of necessary materials, tools, and labor. A single welder might easily cost tens of thousands of dollars.
Furthermore, even knowing how to weld is a difficult task. Many welders obtain certification and continue their study at accredited universities.
Welding is a procedure that joins two metal surfaces together to form a strong bond.
This is critical in cases where the bond must withstand a lot of stress. This can include joining the components of an automobile, watercraft, or piece of machinery.
In many circumstances, however, an alternative to welding is preferable, as a strong bond isn’t always necessary.
Ways To Bond Metal To Metal Without Welding
Learning how to combine metals without welding is not difficult. For joining metals, there are a metal of non-welding methods.
Some require heat, but at lower temperatures, while others rely on diverse adhesive methods.
Let’s look at how to join two metal parts together without requiring welding.
Nanomaterials
Nanomaterials, also known as nanoscale sculpting, are a still-evolving means of mixing metals.
It requires roughening the metal surface with a sophisticated etching method that uses electrochemistry and 3D printing to accomplish.
This results in the creation of a delicate hook-like structure on a very small scale. After that, the glue is utilized to join two of these surfaces together, resulting in a very strong bond.
This technology can be used to connect massive, heavy components in industries such as automotive and shipbuilding.
It eliminates the use of high temperatures, which can harm surfaces, especially those that have been coated or painted.
Nanoscale sculpting, on the other hand, maybe performed at room temperature and requires fewer safety precautions.
As the technology advances, this approach could be used in a variety of applications, including medical technology.
Pros
- At room temperature, the technique is carried out.
- Heat-based methods are more dangerous.
- Increases the strength of the bond between surfaces
- Has the ability to work in a range of environments
Cons
- The strategy is still in the works and hasn’t been properly tested.
Glue

Using glue to learn how to weld metal without a welder is a fantastic hack. Glue is a simple way to join two metal surfaces. It requires applying an adhesive to the surfaces to be connected before pushing them together to form a bond.
A number of adhesives, including silicone-based, epoxy, polyurethane, and even double-sided tape, can be used to adhere metals.
For this reason, a slew of new items are being developed. Nanorods with varied metallic cores are found in some adhesives.
The various metallic cores fuse together to form a strong bond after this chemical is applied to the surfaces to be joined.
Pros
- Heat-based solutions are more expensive than glue.
- There is less risk involved in the use of adhesives.
Cons
- Because gluing metal surfaces together creates weaker connections than other heating methods, it isn’t appropriate for all applications.
Soldering
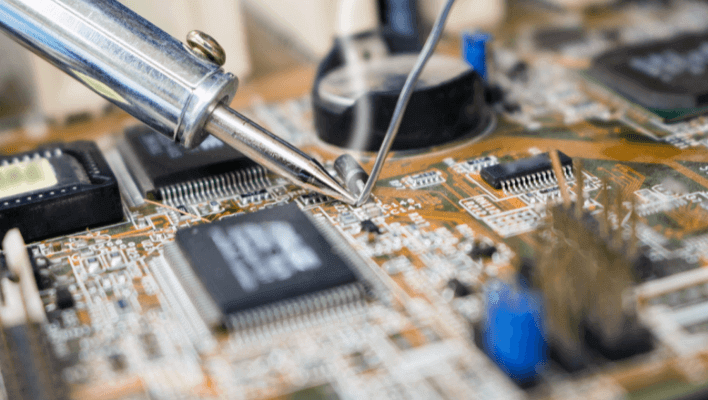
Soldering resembles welding in appearance, but it actually creates an electrical rather than a mechanical connection between metals. This signifies that the bond’s structural integrity is compromised.
Solder is a substance that has the appearance of coiled wire. It’s a soft metal alloy, meaning it’s made up of many metals.
A typical solder is 99 percent tin, but it may also contain other metals such as copper, silver, zinc, and bismuth.
Soldering requires less heat than welding since this alloy melts at a low temperature.
Soldering melts the filler metal, which is then used as an intermediary bond, rather than the metal portions that will be joined.
Soldering is a highly effective method for electrical circuits. Different components in a circuit include small devices like transistors, resistors, capacitors, and LEDs. Each one serves a distinct purpose.
These devices are connected to supply a wide range of parts for electrical devices such as calculators, radios, televisions, and computers.
The efficacy and dependability of an electronic connection in a circuit are improved by soldering.
Pros
- Safe than Welding.
- A bond is established at a lower temperature.
- Provides a circuit-based gadget with an electrical connection.
Cons
- It creates an electrical connection instead of a stronger mechanical connection.
- It can’t be used in a lot of applications because of the weaker bond.
Brazing
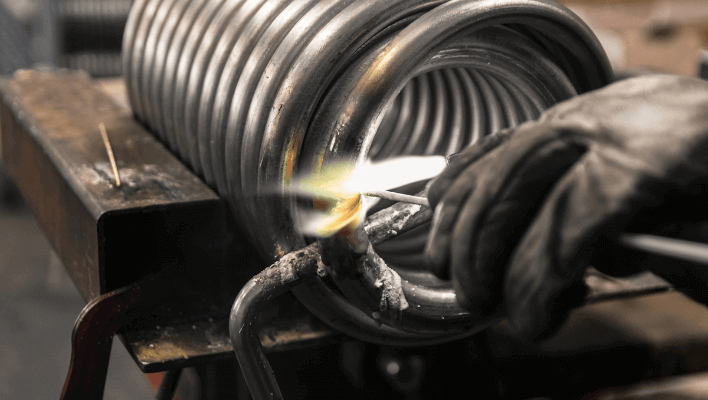
Learning how to connect two steel pipes without welding is a little more difficult.
Brazing, like welding and soldering, is a method of fusing two pieces of different metal together by melting them together. This is a wonderful way to learn how to attach metal to metal using the proper tools.
When brazing, the filler metal functions more like an adhesive. The filler component for brazing can be made of a number of metals depending on the application.
Listed below are a few examples:
- Copper-phosphorus
- Silver
- Aluminum-silicon
- Magnesium
- Cobalt
- Nickel
- Precious alloys
Because these materials have a higher melting point than tin, brazing is done at a higher temperature than soldering.
This means that the filler metal holds the metals together securely while the heat impacts them.
Because the soldering temperature is too low, the metal surfaces do not melt; instead, the solder rests between them and makes the connection.
As a result, brazing is a cross between soldering and welding. The filler element melts the metal surfaces together, giving in a strong mechanical attachment.
This method can be used to learn how to bond aluminum without welding.
Pros
- Similar to welding, it creates a strong mechanical bond.
- This operation is performed at a lower temperature than welding.
- Adaptable to a variety of uses
Cons
- The join is not as strong as welding because of the softer filler metal.
Riveting
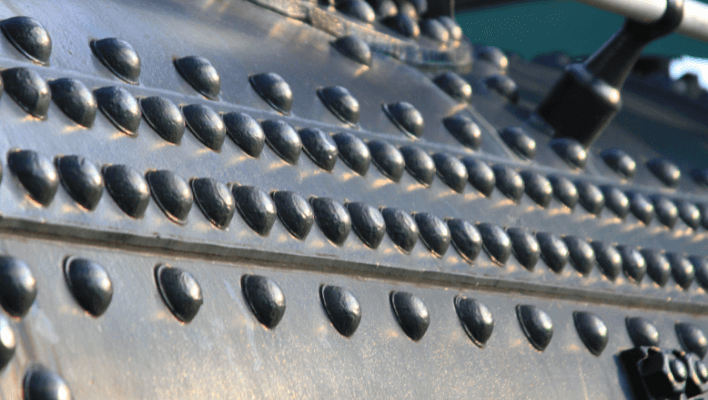

Riveting is the process of utilizing mechanical fasteners to produce a permanent bond between two metal surfaces. It’s a straightforward sheet metal joining procedure.
It has a cylinder-shaped shaft and a head on one end, similar to a screw or a nail. This is inserted into a pre-drilled hole and pounded until the rivet’s tail flattens and expands to the size of the shaft.
The rivet’s thicker end secures it in place, allowing it to attach two metal surfaces without the use of heat or glue.
This method is appropriate for tension loads where they connection must also withstand opposing forces. Bolts and screws, on the other hand, are the preferred method of tension load support in general.
Riveting is ideal for shear loads that are perpendicular to the axis of the rivet shaft.
It’s widely used in construction projects where strong linkages between lightweight materials are required. It’s also used in the construction of vehicle chassis.
Riveting is frequently preferred over welding when mixing sheet metal alloys since the extreme heat can cause the metal to bend and change its material properties.
Pros
- Provides excellent support for shear stress.
- This is preferable than welding for joints that will be subject to vibration and impact pressures.
- It is not necessary to use heat.
- It’s primarily useful for joining lightweight metal pieces together.
Cons
- Leaks can cause gaps in joints, which are not impervious to leaks.
Welding Fundamentals
Welding is the process of joining two metal pieces together to form a strong bond.
During this procedure, you can add a filler or a flux while applying heat.
A filler is a little piece of metal that is delivered by a welding rod and fills in any gaps between two metal surfaces.
When molten metal comes into contact with gas in the air, it forms oxides or nitrates, which can weaken the bond. Flux is a non-metal chemical that prevents this from happening.
Welding is a heat-based method of joining metals.
Only a few examples of probable sources include oxyacetylene gas, electrodes, lasers, ultrasonics, and electron beams.
Final Thoughts
Welding is a method of joining two metal items together to make a strong bond.
While this has many benefits, it can also be costly and dangerous. Welding isn’t always required when it comes to metal bonding.
We’ve prepared a list of metal joining methods that can be used instead of welding. There are benefits and drawbacks to each, but there is something for everyone.
Hopefully, you’ll be able to find the right process now, regardless of what type of metal you’ll be joining.
FAQs

With 8 years of experience a senior welding instructor and safety equipment researcher and writes articles, reviews and guidelines on helmets and other welding and safety gears at Welder Choice, and other written works have been published in various publications.